2421 Tech Center Court Las Vegas, Nevada 89128
NV CONTRACTORS LIC # 62375 Bid Limit $1.4M CITY OF LV PRIVILEGE LIC # P66-00352

NV CONTRACTORS LIC # 62375 Bid Limit $1.4M CITY OF LV PRIVILEGE LIC # P66-00352
2421 Tech Center Court Las Vegas, Nevada 89128
NV CONTRACTORS LIC # 62375 Bid Limit $1.4M CITY OF LV PRIVILEGE LIC # P66-00352

NV CONTRACTORS LIC # 62375 Bid Limit $1.4M CITY OF LV PRIVILEGE LIC # P66-00352


The simple answer:
CAT-5 is rated to 100M
CAT-5e is rated to 350M
CAT-6 and CAT-6e is rated to 550M or 1000M depending on your source
CAT-6 cable is made with 23 gauge conductor wire as opposed to the slightly smaller 24 gauge for CAT-5e and also has a separator to handle crosstalk better.
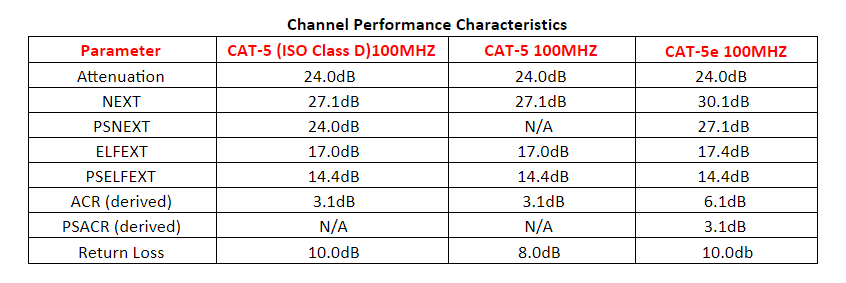
Both CAT-5 and CAT-5e have 100 ohm impedance and electrical characteristics supporting transmission up to 100 MHZ. The difference between CAT-5 and CAT-5e show in all aspects of performance: frequency, resistance, attenuation and NEXT. CAT-5 components were designed with high-speed gigabit Ethernet in mind. While CAT-5 components may function to some degree in a gigabit Ethernet, they perform below standard during high-data transfer scenarios. CAT-5e cables work with ATM and gigabit speed products. Simply, if you are using a 100Mbps switch, get CAT-e cable instead of CAT-5.
CAT-5e is formally called ANSI/TIA/EIA 568A-5 or simply CAT-5e (the e stands for “enhanced”). CAT-5e is completely backward compatible with current CAT-5 equipment. The enhanced electrical performance of CAT-5e ensures that the cable will support applications that require additional bandwidth, such as gigabit Ethernet or analog video.
UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair. It is a cable type with pairs of twisted insulated copper conductors contained in a single sheath. UTP cables are the most common type of cabling used in desktop communications applications.UTP stands for Unshielded Twisted Pair. It is a cable type with pairs of twisted insulated copper conductors contained in a single sheath. UTP cables are the most common type of cabling used in desktop communications applications.
Stranded cable has several small gauge wires in each separate insulation sleeve. Stranded cable is more flexible, making it more for shorter distances, such as patch cords.
Solid has one larger gauge in each sleeve. Solid cable has better electrical performance than stranded cable and is traditionally used for inside walls and through ceilings – any type of longer run of cable.
Patch cables are made of stranded copper conductors for flexibility. This construction is great for the flexing and the frequent changes that occur at the wall outlet or patch panel. The stranded conductors do not transmit data signals as far as solid cable. The TIA/EIA 568A which is the governing standards regarding commercial cabling systems limits the length of patch cables to 10 meters in length. Does that mean you can’t use stranded cable for longer runs? No, not at all, we’ve seen installations running stranded cable over 100 feet with no problem – it’s just not recommended.
10 BASE-T is the IEEE standard that defines the requirement for sending information at 10 Mbps on unshielded twisted-pair cabling, and defines various aspects of running Ethernet on this cabling.
100BASE-T is the IEEE standard that defines the requirement for sending information at 100 Mbps on unshielded twisted-pair cabling, and defines various aspects of running baseband Ethernet on this cabling.
1000BASE-T (also called gigabit Ethernet) is the IEEE standard that defines the requirement for sending information at 1000 Mbps on unshielded twisted-pair cabling, and defines various aspects of running baseband Ethernet on this cabling.
A cross-over cable is a segment of cable that crosses over pins 1 & 2 and 3 & 6. This cable is normally used to connect two PC’s without the use of a hub, or can be used to cascade two hubs without using an uplink port. Some DSL modems require a crossover cable to the PC or hub to which they are connected.
For solid UTP:
Fast Ethernet 100BASE-T 100 meters (328 feet)
Twisted pair Ethernet 10BASE-T 100 meters (328 feet)
Recommended maximum lengths for patch cables made from stranded cable:
Fast Ethernet 100BASE-T 10 meters (33 feet)
Twisted pair Ethernet 10BASE-T 100meters (33 feet)
Yes. It works with any 10BASE-Tor 100BASE-T network card and hubs. CAT-5 is also upwardly compatible with CAT-5e, however your network throughout will only be as fast as the slowest part.
Operating temp for CAT-5e cable: -10c to 60c
T568A and T568B are the 2 wiring patterns for 8 position RJ45 modular plug, both permitted under the TIA/EIA 568A wiring standards document. The only difference between the two patterns is that the pairs 2 (orange) and 3 (green) are interchanged.
There are three levels. General purpose: UL1581; Riser: UL1666; and Plenum: UL910. These numbers are all fire and safety rated.
EMI standards for Electro-Magnetic Interference. It is potentially harmful to you communications system because it can lead to signal loss and degrade the overall performance of high-speed, CAT-5e cabling. EMI is interference in signal transmission or reception and is caused by the radiation of electrical or magnetic fields which are present near power cables, heavy machinery or fluorescent lighting.
Avoiding EMI is as simple as not laying your network cable within 12’ of electrical cable or if needed switching from UTP to more expensive shielded cable.


